About biochar
A brief overview
Biochar: a versatile helper for the soil, climate and environment
Production and composition
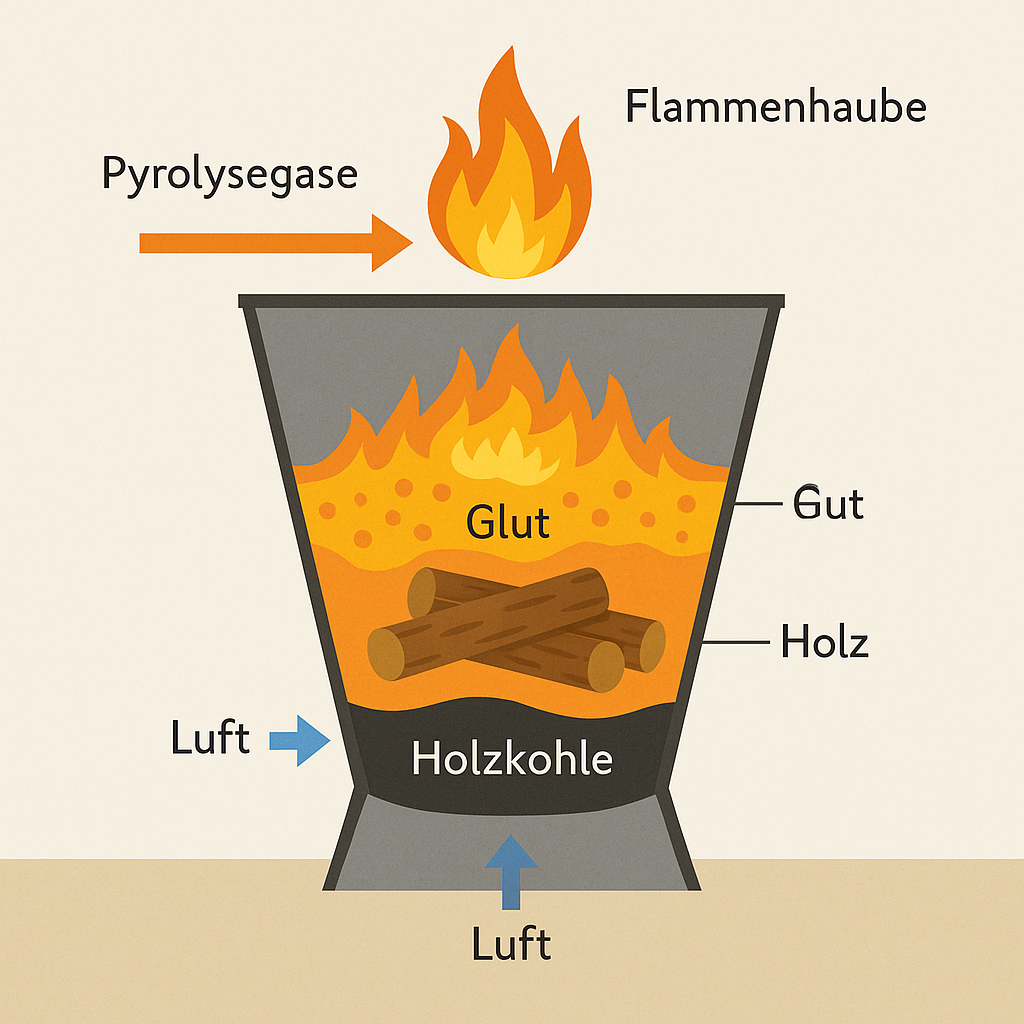
Biochar is produced by pyrolysis – a process in which plant materials such as wood, green waste or agricultural residues are carbonized at temperatures between 380°C and 1000°C in the absence of air.
The result is a porous, carbon-rich substance with a high internal surface area that can bind water, nutrients and pollutants.
Application examples in practice
Biochar, also known as biochar, has many exciting applications in practice – especially in agriculture, but also in other industries. Here are some examples of how biochar is used:
Agriculture & Horticulture
-
Main objective: Improvement of soil structure and fertility.
-
Effect: Increased water storage capacity, nutrient retention, promotion of humus formation, reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Practical example: Incorporating biochar into compost or liquid manure to produce Terra Preta-like soils.

Composting
Biochar improves compost quality by retaining nutrients and moisture. It accelerates the rotting process and binds odors, promotes microorganisms and helps to produce fertile humus. Simply mix it into the compost in layers – for healthy soil and sustainable gardening.

Terra Preta
Biochar is a key component of “Terra Preta”, a fertile black soil discovered in the Amazon region. It is created by mixing compost, biochar and organic waste. Ideal for gardens that need to be sustainable and productive.
This technique is now being imitated worldwide to create sustainable and productive soils.

Urban Gardening
In urban areas, biochar is increasingly being used in gardens and on balconies.
Biochar makes raised beds, balcony boxes and plant sacks more fertile in the long term. It stores water and nutrients, improves the soil structure and supports plant growth – ideal for limited growing areas in the city.



Building materials & textiles
-
Main objective: Development of sustainable materials with improved properties.
-
Effect: Insulating effect, moisture regulation, odor absorption.Bochum University
-
Practical example: use of biochar in insulating materials or functional clothing to improve material properties. Bochum University of Applied Sciences

Real projects in the EU and Greece
1st HyPErFarm project (EU)
An EU-funded project that combines agrivoltaics, hydrogen production and biochar to develop sustainable agricultural systems. PK BiG
2. university of Hamburg – biochar research
The University of Hamburg received funding for a project to research the use of biochar in agriculture and its contribution to climate protection.
Conclusion
Biochar is a versatile and sustainable material that offers both ecological and economic benefits. Whether as a soil improver, climate protector or environmental technology – its potential applications are diverse and promising. Through the targeted use of biochar, we can not only improve the quality of our soil, but also make an important contribution to climate protection.
| Criterion | Classic pyrolysis (retort) | Kon-Tiki (open pyrolysis) |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen supply | Completely airtight, no oxygen | Limited oxygen supply (especially at the top), but not airtight |
| Construction | Closed container, often made of metal | Funnel-shaped open tank, often made of steel |
| Heat source | Externally heated (gas, electricity, flame) | Self-burning through the addition of fuel |
| Process control | Very precise, industrially controllable | Manually controlled by timing and replenishment |
| Product | High-purity biochar, possibly by-products (tar, gas) | Good quality biochar, somewhat more variable |
| Smoke development | Low (sealed combustion in combustion chamber) | Very low – thanks to flame hood, if operated correctly |
| Application/Scaling | Industrial, laboratory, large quantities | Decentralized, small to medium quantities, ideal for gardens |
| Costs/effort | High, complex, expensive | Inexpensive, simple, suitable for DIY |
| Topic | Title & Link | Description |
| Goal & effect | Biochar in agriculture – opportunities and risks | Comprehensive report on the use of biochar in agriculture, including animal husbandry. Discusses potentials and challenges. |
| Effect | Biochar in agriculture | Report by the Federal Office for Agriculture on the use of biochar as a feed additive, stable bedding and manure additive. |
| Practical examples | Biochar in animal husbandry – Carbex | Practical information on the use of biochar in animal husbandry, including study results. |
| Topic | Title & Link | Description |
| Purpose & Effects | Beneficial impacts of biochar as potential feed additive in animal husbandry | Scientific paper exploring the benefits of using biochar as a feed additive in livestock farming. |
| Effects | Effects of feeding a pine-based biochar to beef cattle | Study on how biochar affects emissions, digestion, and composting in beef cattle. |
| Practical examples | The use of biochar in cattle farming | Article with real-world examples of biochar applications in cattle farming, including improvements in manure management and animal health. |
| Θέμα | Τίτλος & Σύνδεσμος | Περιγραφή |
| Σκοπός & Επιδράσεις | Σύνθεση προηγμένων υλικών από βιομάζα | Πτυχιακή εργασία που περιγράφει την αξιοποίηση της βιομάζας για παραγωγή υλικών όπως η φυτική άνθρακας με αναφορές στη χρήση στην κτηνοτροφία. |
| Επιδράσεις | Υπουργείο Περιβάλλοντος και Ενέργειας | Πληροφορίες για την επίδραση της φυτικής άνθρακα στη μείωση οσμών και βελτίωση της υγείας των ζώων. |
| Πρακτικά Παραδείγματα | Πτυχιακή εργασία – Χλόη Ασπασία Ράντζου | Περιέχει μελέτες περιπτώσεων για την εφαρμογή της φυτικής άνθρακα σε αγροτικές και κτηνοτροφικές δραστηριότητες. |
| Topic | Title & Link | Description |
| Goal & effect | Biochar in agriculture: opportunities and challenges | This report by the Institute of Rural Structures Research analyzes the potential uses of biochar in agriculture, including its impact on soil fertility and climate protection. |
| Effect | Biochar boosts crop yields and increases fertilizer efficiency | An article describing the positive effects of biochar on crop yields and fertilizer use. |
| Practical examples | Cascading use of biochar in agriculture | Report on the multiple use of biochar in various agricultural applications to maximize its benefits. |
| Current projects | Biochar in arable farming – LfL Bayern | Information on current research projects in Bavaria on the use of biochar in arable farming. |
| Topic | Title & Link | Description |
| Purpose & Impact | Climate-Positive Farming Reviews | A review by the James Hutton Institute on the potential of biochar and pyrolysis as climate-positive technologies in Scottish upland farming. |
| Impact | Biochar to Remove Carbon – University of Nottingham | Details on the UK’s largest trial evaluating biochar’s viability for carbon sequestration in agriculture. |
| Practical Examples | Re-Generation Earth Biochar Collaboration – University of Kent | A project demonstrating efficient on-farm biochar production and its benefits for soil productivity and climate change mitigation. |
| Current Projects | Carbon Gold – Leading the Way in UK-Derived Biochar | An initiative focusing on the development and application of biochar products to improve soil health and sequester carbon. |
| Θέμα | Τίτλος & Σύνδεσμος | Περιγραφή |
|---|---|---|
| Σκοπός & Επίδραση | Δυνατότητες και κίνδυνοι της γεωργίας άνθρακα | Άρθρο που αναλύει τις δυνατότητες και τους κινδύνους της γεωργίας άνθρακα στην Ελλάδα, εστιάζοντας στη χρήση φυτικής άνθρακα για τη βελτίωση της γονιμότητας του εδάφους και τη δέσμευση άνθρακα. |
| Επίδραση | Γεωργία άνθρακα – Οι βασικές αρχές | Εισαγωγικό άρθρο που παρουσιάζει τις βασικές αρχές της γεωργίας άνθρακα και τη σημασία της φυτικής άνθρακα στης βιώσιμη γεωργία. |
| Πρακτικά Παραδείγματα | Αναγεννητική γεωργία στην Ελλάδα | Παρουσίαση αγροκτήματος στην Ελλάδα που εφαρμόζει πρακτικές αναγεννητικής γεωργίας, συμπεριλαμβανομένης της χρήσης φυτικής άνθρακα. |
| Τρέχοντα Έργα | Η γεωργία άνθρακα έρχεται στην Ελλάδα | Άρθρο που αναφέρεται στην εισαγωγή της γεωργίας άνθρακα στην Ελλάδα και τις σχετικές πρωτοβουλίες. |
